What is Blockchain Technology? How Does It Work
Introduction-
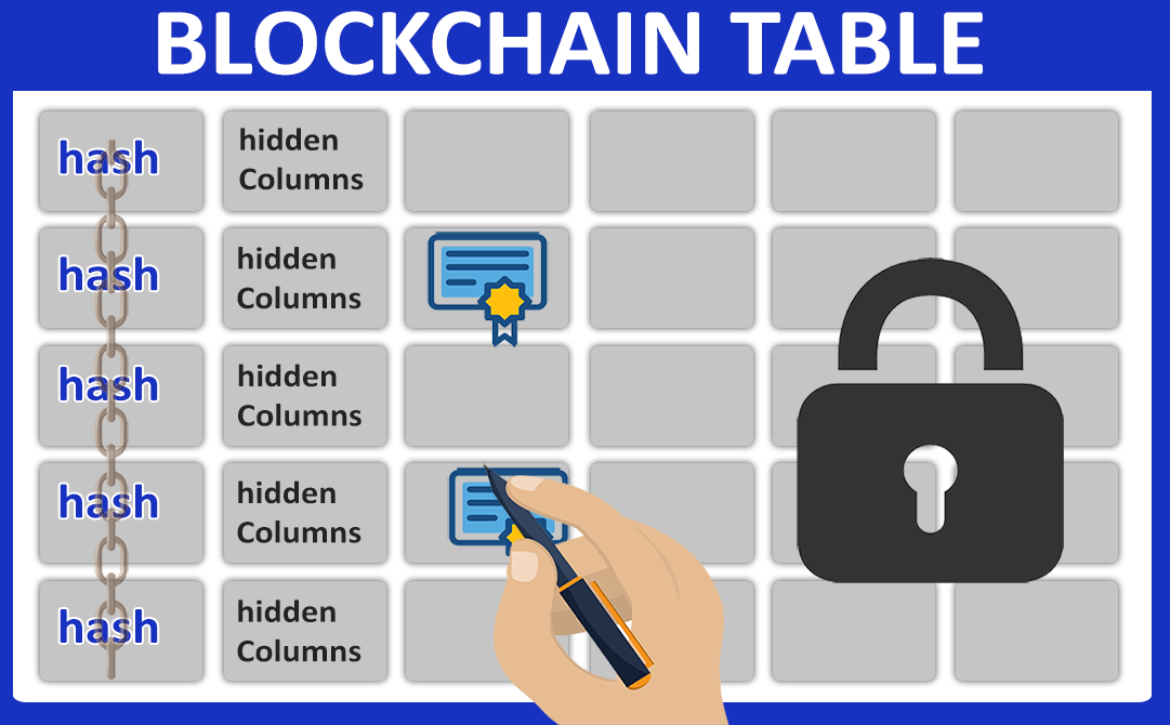
A blockchain is a digital ledger of transactions protected from hacking and modification by a network of computers. With the help of technology, people can transact with one another securely without the need for a middleman like a bank, government, or another third party. Cryptography is used to link together blocks, a set of records. Peer-to-peer computer networks independently verify each transaction, time-stamp it, and then add it to the ledger. Data cannot be easily changed once it has been captured. Blockchain technology has gained popularity with the increasing use of Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies, but it also has promising uses in the legal sector, real estate transactions, the medical field, and any other sector that requires the authorization and documentation of a series of actions or transactions.
How Does Block chain Work?
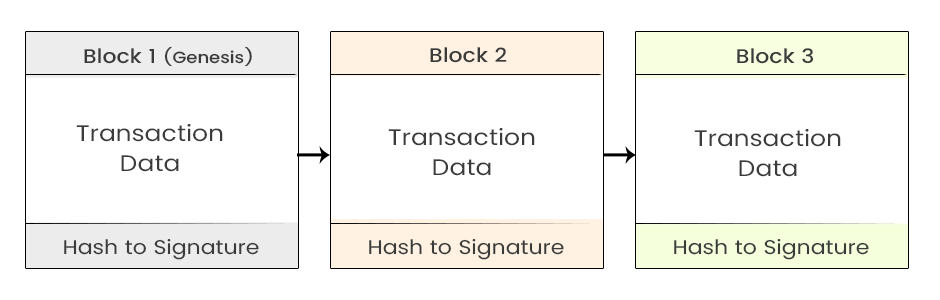
The name “blockchain” is not by chance: The digital ledger is sometimes depicted as a “chain” made up of distinct data “blocks.” A new “block” is made and attached to the “chain” each time new data is added to the network on a regular basis. To achieve this, all nodes must update their copies of the blockchain ledger to match one another. Blockchains are also referred to as distributed ledger technologies.
Advantages of block chain:
Higher Accuracy of Transactions:
This can lower errors because a blockchain transaction needs to be confirmed by several nodes. The other nodes would notice something is off and recognise the error if one node has a database error. In contrast, if a mistake is made in a traditional database, it may be more likely to be accepted. Additionally, each asset is uniquely identifiable and recorded on the blockchain ledger, eliminating the possibility of double spending.
No Need for Intermediaries:
Blockchain enables two parties to a transaction to confirm and finish it directly between themselves. This saves time and money on paying a middleman, such as a bank. “It has the potential to promote financial empowerment for the unbanked or under-banked populations of the world, to increase the efficiency of all digital transactions, and to fuel a new generation of internet apps,”
Extra Security:
Theoretically, it is nearly impossible to conduct fraudulent transactions on a decentralized network like blockchain. They would have to hack each node and modify each ledger in order to add fake transactions. While not strictly impossible, many cryptocurrency blockchain systems use proof-of-stake or proof-of-work transaction verification techniques, which make it challenging and not in the participants’ best interests to add fraudulent transactions.
More Efficient Transfers:
People may move assets and money more effectively because blockchains are available around-the-clock, especially when doing so overseas. There is no need for them to wait days for a bank or a government organization to manually authenticate everything.
Conclusion:
Blockchain innovation could be very reciprocal in a chance space for the future world that incorporates both unified and decentralized models. Like any new innovation, the blockchain is a thought that at first disturbs, and over the long run it could advance the improvement of a bigger environment that incorporates both the prior way and the new development. Hence, after some time, blockchain innovation could exist in a bigger biological system with both unified and decentralized models.